
|
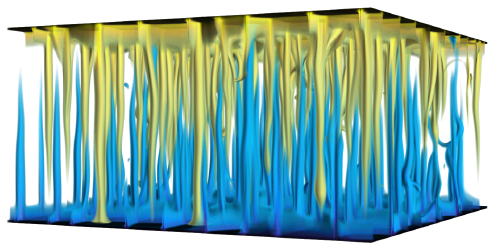
Double Diffusive Convection DDC refers to the buoyancy-driven flow with fluid density depending on two scalar components with very different molecular diffusivities. DDC is omnipresent in Oceanographic, Astrophyscal, and Geophysical environments. We conducted direct numerical simulations and develop theoretical models to understand the evolution of flow morphology and transport properties. |
|
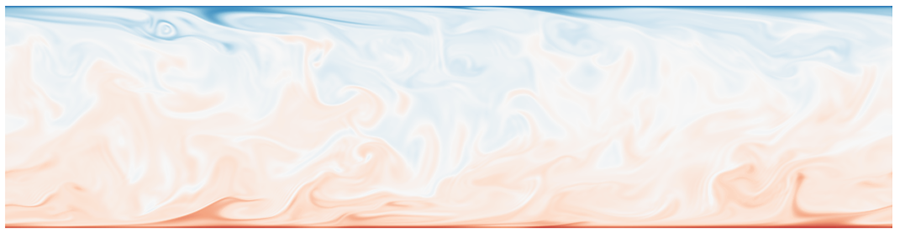
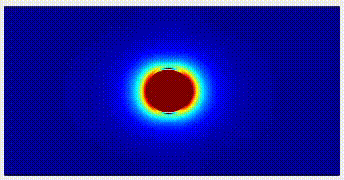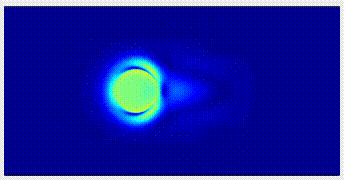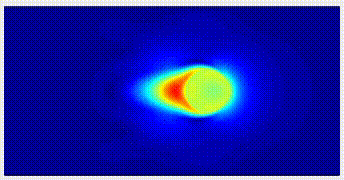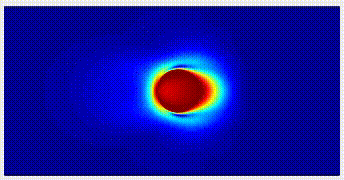
Scalar Turbulence Turbulent flows with scalar components are of significant engineering applications, and important model for studying the physical mecahnism of turbulence. We carry out direct numerical simulations about wall turbulence, and investigate the mixing and transport properties of turbulent flows. |
|
Immersed-Boundary Method IB method is very effective and popular for simulating flow-structure interaction and multiphase flows, due to its simplicity in dealing with the complex geometry and deformation of boundary. We develop new techniques to reduce the numerical error at boundary in IB method, and utilize the method to simulate various complex flows. |
|
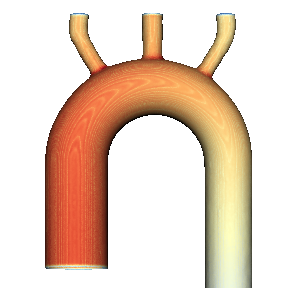
Hemodynamics The blood flow in aorta has relatively high Reynolds number, and very complex geometry. With the numerical method developed in our group, we conduct direct numerical simulations about the aorta hemodynamics. We collaborate with clinic surgeon and seek the applications of CFD in treating the related diseases, such as aorta dissection. |
|
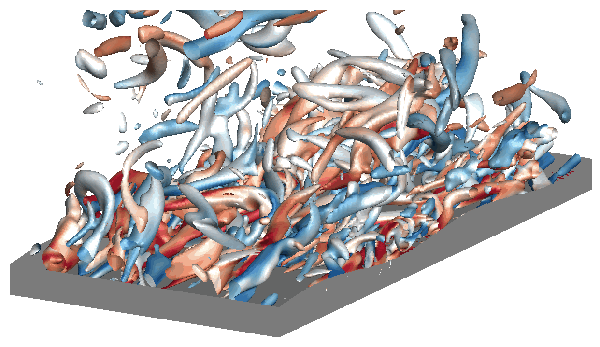
Flow Control Flow control and turbulent drag reduction have long been the active research area due to their huge potential in engineering flows. We utlized IB method and investigate the drag reduction by deforming boundary. We also study the enhancement of scalar transport by boundary deformation. |