开发具有高选择性、兼具多种成像模态为一体的、具有适宜的生物分布和药代动力学特性、低毒安全的成像探针是多模态分子影像技术的重要内容。
纳米颗粒优异的表面特性为同时搭载多种功能性的基团,实现不同模态的集成提供了可能;同时其在肿瘤部位的透过性增强与滞留(EPR)效应,使其具有被动靶向肿瘤的特性;此外,一些纳米材料兼具优异的光学、磁学特性,因此本实验室致力于开发基于纳米材料的多模态分子影像探针。我们拟采用纳米颗粒作为平台,借助合成与转化技术赋予其分子影像功能,改善其生物分布与靶向能力,降低其毒性,获得性能优越的可工程化成像探针。
基于荧光量子点的新型分子探针
荧光量子点具有合适的尺度和优异的荧光特性,在生物医学成像领域具有广泛的应用前景。但是长期以来水溶性差、生物相容性不良等问题限制了其在该领域的实际应用。我课题组成功采用新型的透明质酸-巯基乙胺聚合物对量子点进行包覆,获得了水溶性良好,能够在大pH范围(2-12)长时间保持稳定的量子点。并且通过细胞实验证实了其良好的生物相容性和对CD44+肿瘤细胞的靶向特性。进一步将在此平台上搭载多种成像模态,制备出多模态分子影像探针。
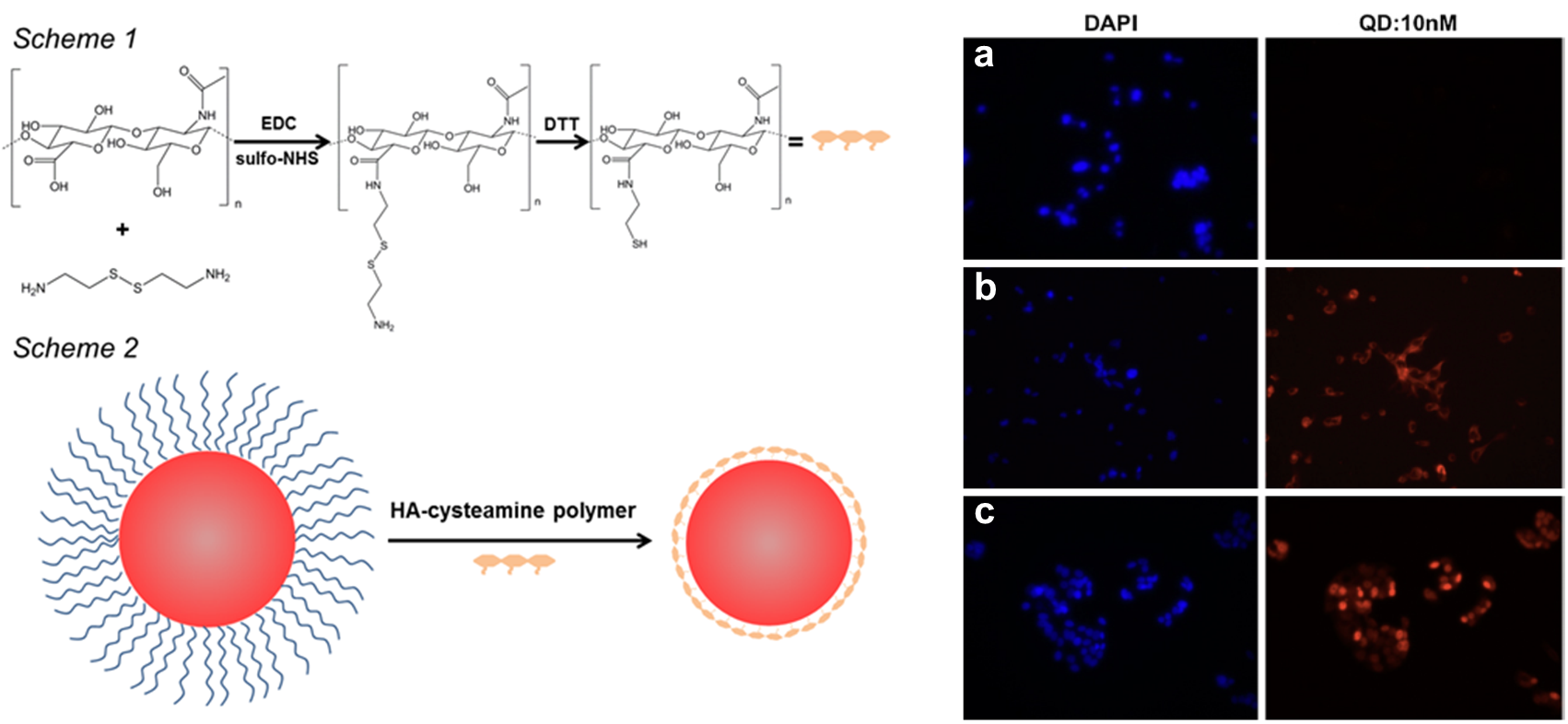
(Fig.1)
基于聚多巴胺的新型表面修饰手段
多巴胺分子在碱性条件下可以被氧化发生自聚合反应,形成聚多巴胺。利用聚多巴胺易于在纳米颗粒表面包覆的特性,以及其具有光学吸收、离子络合、表面功能化的性质,我们拟构建具有分子靶向特性的,集成PET、CT、SPECT、PAT、MRI多种模态为一体的多模态分子影像探针。
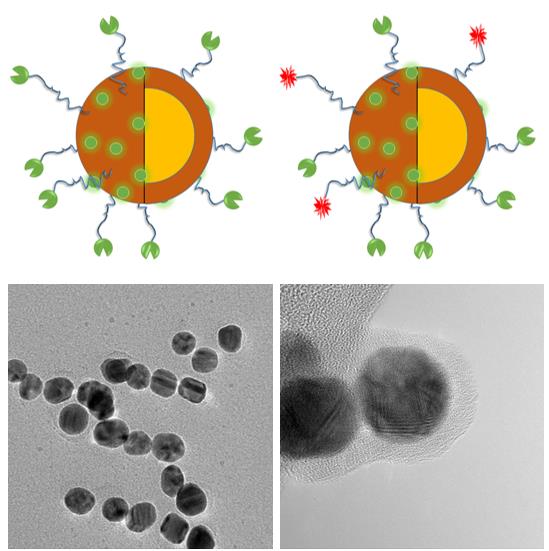
(Fig. 2)
采用PET/CT的新成像探针的临床应用评估研究
18F-Fallypride和11C-CFT是示踪多巴胺神经传递的PET影像探针,对于多种神经精神障碍,如帕金森氏症,注意力缺陷多动障碍(ADHD),抗精神病药恶性综合症以及药物和酒精依赖的诊治具有重要应用前景。另外,18F-ML-10是一种细胞凋亡的生物标记物,可用于肿瘤治疗效果的评估。与301医院合作,采用基于我课题组的核心技术研发的Rayscan-64 PET / CT系统开展了对三种新探针的临床应用评估。
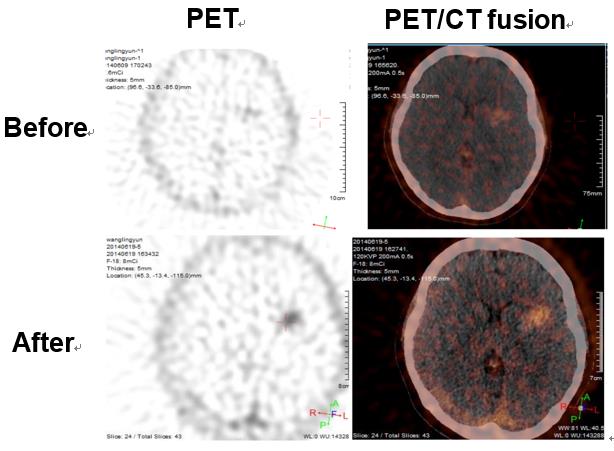
(Fig. 3)
基于PET/SPECT/CT/荧光四模态成像的肿瘤分型研究
肿瘤的不同亚型之间存在着分子表达水平的差异,其生物学行为在宏观上也具有特征的差异,开展对肿瘤不同亚型的分型研究对于基础医学研究,以及临床的诊断和治疗都具有重要的价值。我们通过PET/SPECT/CT/荧光四种模态成像,在分子水平上揭示了两种结直肠癌亚型的特征区别。
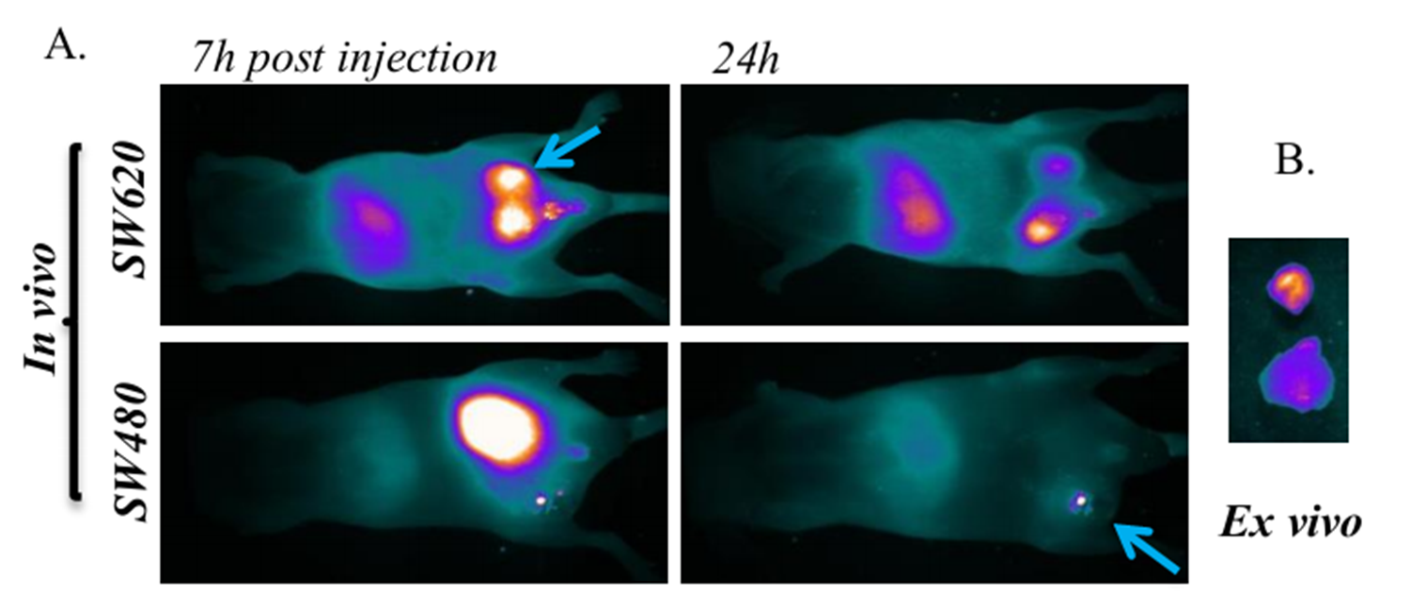
(Fig. 4)
One of our main research focuses is to develop highly specific on multi-modality imaging probes with possessing biodistribution profile and suitable pharmacokinetics, as well as low toxicity.
Nanomaterials demonstrate a lot of merits derived from their nano-scale dimensions. One of the merits that shared by most nanoparticles is the enhanced permeation and retention (EPR) effect, which renders them the innate capability to passively target solid tumors. Some nanoparticles have excellent optical and chemical properties. The superior properties of nanoparticles have enabled the readily surface modification with multiple functional moieties to realize combination of different imaging modalities and therapeutic agents. Therefore, our group aims at the developing of multi-modality molecular imaging probes based on various nanoparticles. We hope to take the advantage of the nanoparticle as drug-carrier platform, to render the probe multiple molecular imaging functionalities through synthesis and transformation, while improving its biodistribution and targeting ability. Have their toxicity mitigated we acquired engineered imaging probe with superior properties.
Novel multi-modality imaging probes based on fluorescent quantum dots
Fluorescent quantum dots (QDs) possess desirable sizes and superior fluorescent properties that enabled them with great potential for applications in biomedical imaging. However, poor water solubility and unsatisfactory biocompatibility have lied on their way to clinics over a long period. We have successfully prepared a novel hyaluronic acid-cystamine polymer coated QDs, which demonstrated improved water solubility as well as excellent stability over a large pH range (2-12) for as long as 140 days. The in vitro experiment shows great biocompatibility and highly specific CD44+ cancer cell targeting capability with mitigated toxicity. We are currently working on the loading of various imaging tags onto this platform for a multi-modality imaging probe.

Figure 1. Left: Schematic illustration of the preparation of HA-cysteamine polymer coated QDs. Right: Targeting of cancer cells with the HA-cysteamine polymer coated QDs. (a) NIH/3imaging T3 fibroblast cell line shows no QD fluorescence and little non-specific binding. (b) MD-MB-231 breast cancer cell line shows strong QD fluorescence of targeted staining. (c) MCF-7 breast cancer cell line also shows strong QD fluorescence of targeted staining.
Novel surface modification technique via self-polymerization of dopamine
Under alkaline condition, dopamine molecules will undergo self-polymerization to form polydopamine. The polydopamine derved from self-polymerization could coat the surface of nanoparticles and act as a colloidal stabilizer that provides various moieties for further surface modification. Taking advantages of polydopamine’s optical absorption, ion chelating capabilities, we intend to develope a novel conjugation approach and a versatile platform for targeted molecular imaging with combination of various modalities such as PET, CT, SPECT, PAT, and MRI, etc.

Figure 2. Top: Schematic illustration of the polydopamine coated gold nanoparticles and their radiolabeling. Bottom: TEM images of the as prepared polydopamine coated gold nanoparticles.
Evaluation of the therapeutic effect with newly developed PET/CT system
18F-Fallypride and 11C-CFT are PET dopaminergic neurotransmission radiotracers. They are capable for the diagnosis and therapy of several neuropsychiatric disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), neuroleptic malignant syndrome, as well as drug and alcohol dependence. Moreover, 18F-ML-10 is a biomarker for tumor apoptosis. We evaluated these three potential new clinical imaging probes by a Rayscan-64 PET/CT system under the collaboration with the PLA general hospital.

Figure 3. The signal of 18F-ML-10 in the tumor region becomes significantly higher after radiation therapy, indicating more apoptotic cells in this region, thus confirming the therapeutic effect of radiation.
Differentiation of Cancer Subtypes by PET/SPECT/CT/Fluorescence Tetra-modalities Imaging
The molecular expression levels vary by the subtypes of a tumor. And their macro biological behaviors are also diverse. The molecular imaging technology is valuable for both preclinical medicine research and clinical diagnosis and therapy in the subtype differentiation study of tumors. We conducted the differentiation of two colorectal cancer subtypes SW620 and SW480 using PET/SPECT/CT/FRI tetra-modalities.

Figure 4. Fluorescent imaging result of the SW480 and SW620 tumor both (a) in vivo and (b) in vitro. The cancer subtype could be differentiated by analyzing the intensity of the signal.
