微机器智能实验室
(Micromachine Intelligence Laboratory, μ-MIL)
实验室的发展主旨
微机器智能,也称为微尺度人工智能(μ-AI),是微机器功能化的终极目标和最高阶段,被用以使微机器适应微尺度下的动态环境变化及各类特种微操作任务需求。自然界中,微观生命体,如载体DNA、纳米机器bacteriophage、微系统Cell等,都展现了不输宏观生命的优秀智能特性,如柔性原子基纳米机构、精准信息编辑、系统性涌现等。同时,智能在微尺度产生的重要意义在于微尺度效应下超短信息传递距离、超快响应速度、超灵敏感知与响应、超稳定动态运行等,提供微机器以更加优良的动态交互能力。本实验室(μ-MIL)旨在撬动机器、装备、系统的智能化和微型化发展,面向下一代智能微机器发展先进微纳米制造与机器人技术,重点探究微机器智能化实现的关键技术与核心问题,以国家重大需求为导向,为精准医疗、智能制造等各类微尺度工程应用,提供智能微机器解决方案。

实验室的核心定位
构建微尺度交互共融机制,探索微机器智能化的基础理论与关键技术
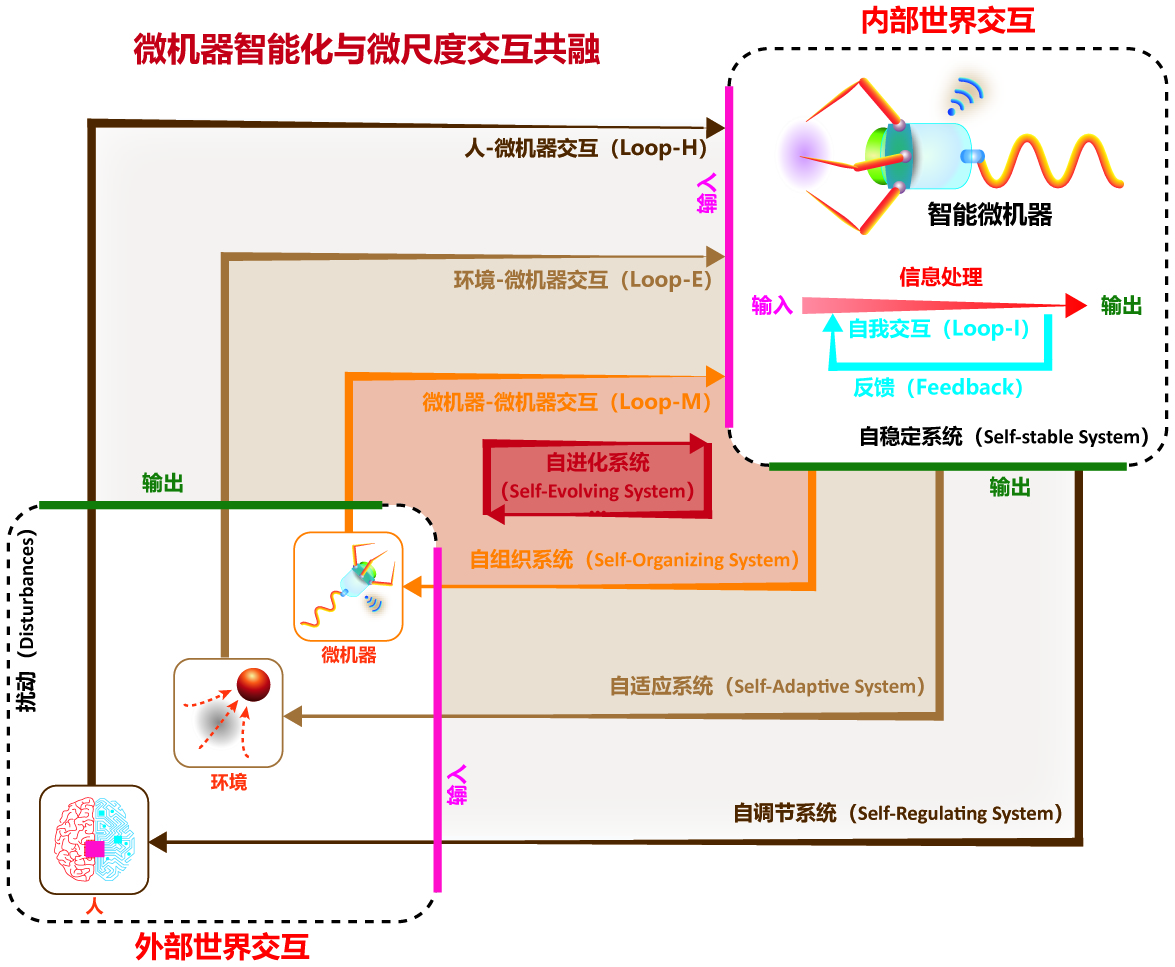
四种交互机制:与自身、人、环境、微机器;
五类微机器智能进化层级:自稳定、自调节、自适应、自组织、自进化系统
实验室的主要研究方向
方向一:微机器智能化技术
软体/连续体微机器
多模态/模块化可重构微机器
柔性微电子集成微机器
微尺度智能感知与信息融合技术
微尺度组装与编辑技术
微机器的群集控制与群集智能
方向二:智能材料与微纳制造技术
智能可打印材料(柔性、刺激响应、生物兼容、可降解等)
微纳4D打印技术(微流控打印、激光直写技术)
微机构-微机电-微电子融合技术
方向三:跨尺度微机器驱控技术
多物理场微纳米机器人驱控技术
驱控系统集成与微型化技术
面向精准医疗的智能微机器靶向递送技术
领域内参考文献

1. Purcell, Edward M. "Life at low Reynolds number." American Journal of Physics 45.1 (1977): 3-11.
2. Nelson J. Bradley, Ioannis K. Kaliakatsos, and Jake J. Abbott. "Microrobots for minimally invasive medicine." Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering 12 (2010): 55-85.
3. Huang T Y, Gu H R, Nelson B J. Increasingly intelligent micromachines. Annual Review of Control Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2022, 5.
4. Cui J Z, Huang T Y, et al. "Nanomagnetic encoding of shape-morphing micromachines." Nature 575.7781 (2019): 164-168.
5. Abbott, Jake J., et al. "How should microrobots swim?." The International Journal of Robotics Research 28.11-12 (2009): 1434-1447.
6. Palagi, Stefano, and Peer Fischer. "Bioinspired microrobots." Nature Reviews Materials 3.6 (2018): 113-124.
7. Luo, Zhaochu, et al. "Current-driven magnetic domain-wall logic." Nature 579.7798 (2020): 214-218.
8. Peterson, John I., and Gerald G. Vurek. "Fiber-optic sensors for biomedical applications." Science 224.4645 (1984): 123-127.
9. Miskin, Marc Z., et al. "Electronically integrated, mass-manufactured, microscopic robots." Nature 584.7822 (2020): 557-561.
10. Hu, Wenqi, et al. "Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion." Nature 554.7690 (2018): 81-85.
11. Douglas, Shawn M., Ido Bachelet, and George M. Church. "A logic-gated nanorobot for targeted transport of molecular payloads." Science 335.6070 (2012): 831-834.
12. Huang, Tian‐Yun, et al. "3D printed microtransporters: Compound micromachines for spatiotemporally controlled delivery of therapeutic agents." Advanced Materials 27.42 (2015): 6644-6650.
13. Jin, Dongdong, et al. "Four-dimensional direct laser writing of reconfigurable compound micromachines." Materials Today 32 (2020): 19-25.
14. Huang, T-Y., et al. "Four-dimensional micro-building blocks." Science Advances 6.3 (2020): eaav8219.
15. Kummer, Michael P., et al. "OctoMag: An electromagnetic system for 5-DOF wireless micromanipulation." IEEE Transactions on Robotics 26.6 (2010): 1006-1017.
16. Yang, Guang-Zhong, et al. "The grand challenges of Science Robotics." Science Robotics 3.14 (2018): eaar7650.
